 Congratulations to Carlee Wright for publishing her second article from her MSc thesis! Click here to read the full article...
Citation: Wright, C.J., Sargeant, J.M., Edge, V.L., Ford, J.D., Farahbakhsh, K., Shiwak, I., Flowers, C., Gordon, A.C., RICG, IHACC Research Team (Berrang-Ford, L., Carcamo, C., Llanos, A., Lwasa, S., Namanya, D.B.), and Harper, S.L. (2018). How are perceptions associated with water consumption in Canadian Inuit? A cross-sectional survey in Rigolet, Labrador. Science of The Total Environment, 618(15): 369–378.
Congratulations to Carlee Wright for publishing her second article from her MSc thesis! Click here to read the full article...
Citation: Wright, C.J., Sargeant, J.M., Edge, V.L., Ford, J.D., Farahbakhsh, K., Shiwak, I., Flowers, C., Gordon, A.C., RICG, IHACC Research Team (Berrang-Ford, L., Carcamo, C., Llanos, A., Lwasa, S., Namanya, D.B.), and Harper, S.L. (2018). How are perceptions associated with water consumption in Canadian Inuit? A cross-sectional survey in Rigolet, Labrador. Science of The Total Environment, 618(15): 369–378.
Abstract
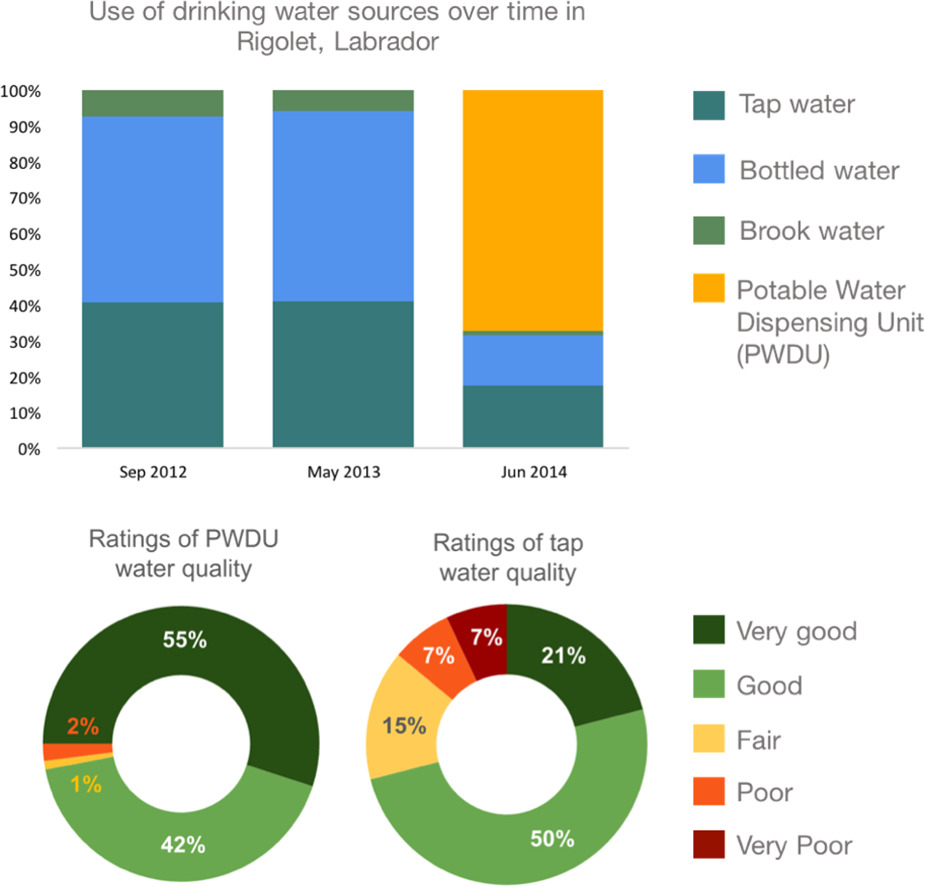
Concerns regarding the safety and aesthetic qualities of one's municipal drinking water supply are important factors influencing drinking water perceptions and consumption patterns (i.e. sources used and daily volume of consumption). In northern Canada, Inuit communities face challenges with drinking water quality, and many Inuit have reported concerns regarding the safety of their drinking water. The objectives of this research were to describe perceptions of municipal tap water, examine use of water sources and changes following the installation of a potable water dispensing unit (PWDU) in 2014, and identify factors associated with water consumption in the Inuit community of Rigolet. This study used data from three cross-sectional census surveys conducted between 2012 and 2014. Principal component analysis (PCA) was used to aggregate data from multiple variables related to perceptions of water, and logistic regressions were used to identify variables associated with water consumption patterns. Three quarters of residents reported using the PWDU after its installation, with concomitant declines reported in consumption of bottled, tap, and brook water. Negative perceptions of tap water were associated with lower odds of consuming tap water (ORPCAcomponent1 = 0.73, 95% CI 0.56–0.94; ORPCAcomponent2 = 0.67, 95% CI 0.49–0.93); women had higher odds of drinking purchased water compared to men (OR = 1.90, 95% CI 1.11–3.26). The median amount of water consumed per day was 1 L. Using brook water (OR = 2.60, 95% CI 1.22–5.56) and living in a household where no one had full-time employment (OR = 2.94, 95% CI 1.35–6.39) were associated with consuming > 2 L of water per day. Results of this study may inform drinking water interventions, risk assessments, and public health messaging in Rigolet and other Indigenous communities.